
Gender:Male
Alma Mater:The Chinese University of Hong Kong
Education Level:Postgraduate (Doctoral)
[MORE] Honors and Titles:2023-05-01 Elsevier/JQSRT Richard M Goody Award
2021-12-01 国家级人才计划青年学者项目
2013-09-01 中国科学院院长优秀奖
Dr. Zeng’s research interests relate to the development of theories and algorithms in two fundamental areas of atmospheric remote sensing: (1) radiative transfer and (2) inverse modeling/satellite retrieval. He led the algorithm development for the JPL-built instrument CLARS-FTS to measure atmospheric trace gases and air pollutants in the Los Angeles megacity, and a JPL-funded research and technology development project to investigate the feasibility for boundary layer measurements of atmospheric isotopologues. Currently, he is leading a research group at PKU to develop a synergetic remote sensing algorithm system that combines the strengths of multiple data sources and radiation/scattering model constraints to get accurate and comprehensive information about atmospheric trace gases from current and future LEO and GEO satellites, including China’s Fengyun series satellites.
[1] Estimating anthropogenic CO2 emissions from China’s Yangtze River Delta using OCO-2 observations and WRF-Chem simulations
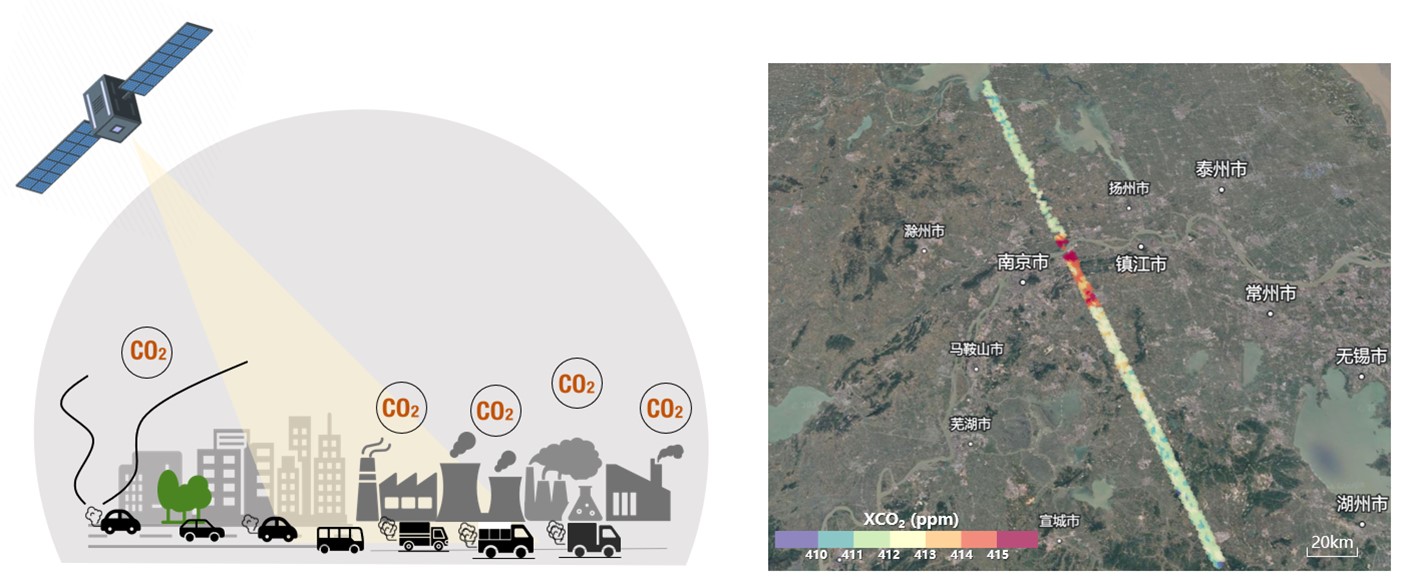
Satellite-based measurements have emerged as an effective method for the top-down estimates of anthropogenic CO2 emissions. Changes in the column-averaged dry-air mole fractions of CO2 (XCO2) in the atmosphere reflect contributions from both human activities and natural processes, posing challenges in accurately extracting anthropogenic XCO2 signals and quantifying urban CO2 emissions. Here, we introduce a novel method based on spatial autocorrelation to directly identify anthropogenic XCO2 signals from satellite measurements of Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2). These signals serve as constraints for atmospheric transport model simulations, enabling the verification of emission inventory over urban areas. Utilizing 35 OCO-2 overpasses over the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration, we demonstrate the effectiveness of local Moran’s I statistics in detecting localized anthropogenic XCO2 enhancements. The results show an average XCO2 increase of 1.36–4.41 ppm in proximity to major cities and areas with intensive industrial activity. A case study near Nanjing, based on eight overpasses, reveals XCO2 enhancements with peaks ranging from 2.26 to 4.72 ppm. To establish the relationship between these XCO2 enhancements and CO2 emissions, we conducted WRF-Chem simulations driven by emis- sions from the Emissions Database for Global Atmospheric Research (EDGAR). Discrepancies between observed and simulated XCO2 enhancements were primarily attributed to uncertainties in the prior emissions, the calculation of urban XCO2 enhancements from OCO-2 data, and complex atmospheric transport dynamics. From our estimates, the daily CO2 emissions in Nanjing is 0.65 ± 0.15 MtCO2/day, which is different from the EDGAR inventory by − 10.5 % to 77.3 % (i.e., 0.17 ± 0.14 MtCO2 /day). Error analysis suggests an uncertainty in CO2 emission estimates associated with XCO2 enhancement and wind speed ranging from 16 % to 32 % (i.e., 0.08–0.15 MtCO2/day). This study proposes an objective approach to assess urban CO2 emissions, leveraging satellite XCO2 observations to improve accuracy and reliability in emission inventories.
Mengya Sheng, Yun Hou, Hao Song, Xinxin Ye, Liping Lei, Peifeng Ma, and Zhao-Cheng Zeng. Estimating anthropogenic CO2 emissions from China's Yangtze River Delta using OCO-2 observations and WRF-Chem simulations. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2025, 316, 114515. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2024.114515.
[2] Diurnal carbon monoxide observed from a geostationary infrared hyperspectral sounder: first result from GIIRS on board FengYun-4B
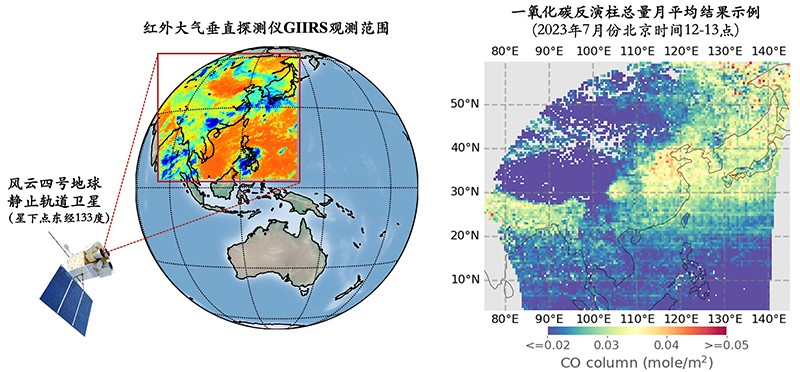
The Geostationary Interferometric Infrared Sounder (GIIRS) on board FengYun-4 series satellites is the world’s first geostationary hyperspectral infrared sounder. With hyperspectral measurement collected from a geostationary orbit covering the carbon monoxide (CO) absorption window around 2150 cm−1 , GIIRS provides a unique opportunity for monitoring the diurnal variabilities of atmospheric CO over eastern Asia. In this study, we develop the FengYun Geostationary satellite Atmospheric Infrared Retrieval (FY-GeoAIR) algorithm to retrieve the CO profiles using observations from GIIRS on board FY-4B, which was launched in June 2021, and provide CO maps at a spatial resolution of 12 km and a temporal resolution of 2 h. The performance of the algorithm is first evaluated by conducting retrieval experiments using simulated synthetic spectra. The result shows that the GIIRS data provide significant information for constraining CO profiles. The degree of freedom for signal (DOFS) and retrieval error are both highly correlated with thermal contrast (TC), the temperature difference between the surface and the lower atmosphere. Retrieval results from 1 month of GIIRS spectra in July 2022 show that the DOFS for the majority is between 0.8 and 1.5 for the CO total column and between 0 and 0.8 for the bottom three layers ranging from the surface to 3 km a.s.l. Consistent with CO retrievals from low-Earth- orbit (LEO) infrared sounders, the largest observation sensitivity, as quantified by the averaging kernel (AK), is in the free troposphere at around 3–6km. The diurnal changes in DOFS and vertical sensitivity of observation are primarily driven by the diurnal TC variabilities. Finally, we compare the CO total columns between GIIRS and Infrared Atmospheric Sounding Interferometer (IASI) and find that the two datasets show good consistency in capturing the spatial and temporal variabilities. This study demonstrates that the GIIRS retrievals are able to reproduce the temporal variability of CO total columns over eastern Asia in the day- time in July. Nevertheless, the retrievals have low detectivity in the nighttime due to their weak sensitivity to the ground level CO changes limited by low information content. Model assimilation that takes into account the retrieved diurnal CO profiles and the associated vertical sensitivity will have potential in improving local and global air quality and climate research over eastern Asia.
Zeng, Z.-C.*, Lee, L., and Qi, C. (2023), Diurnal carbon monoxide observed from a geostationary infrared hyperspectral sounder: first result from GIIRS on board FengYun-4B, Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 16, 3059–3083, https://doi.org/10.5194/amt-16-3059-2023.
[3] Optimal estimation retrieval of tropospheric ammonia from the Geostationary Interferometric Infrared Sounder on board FengYun-4B
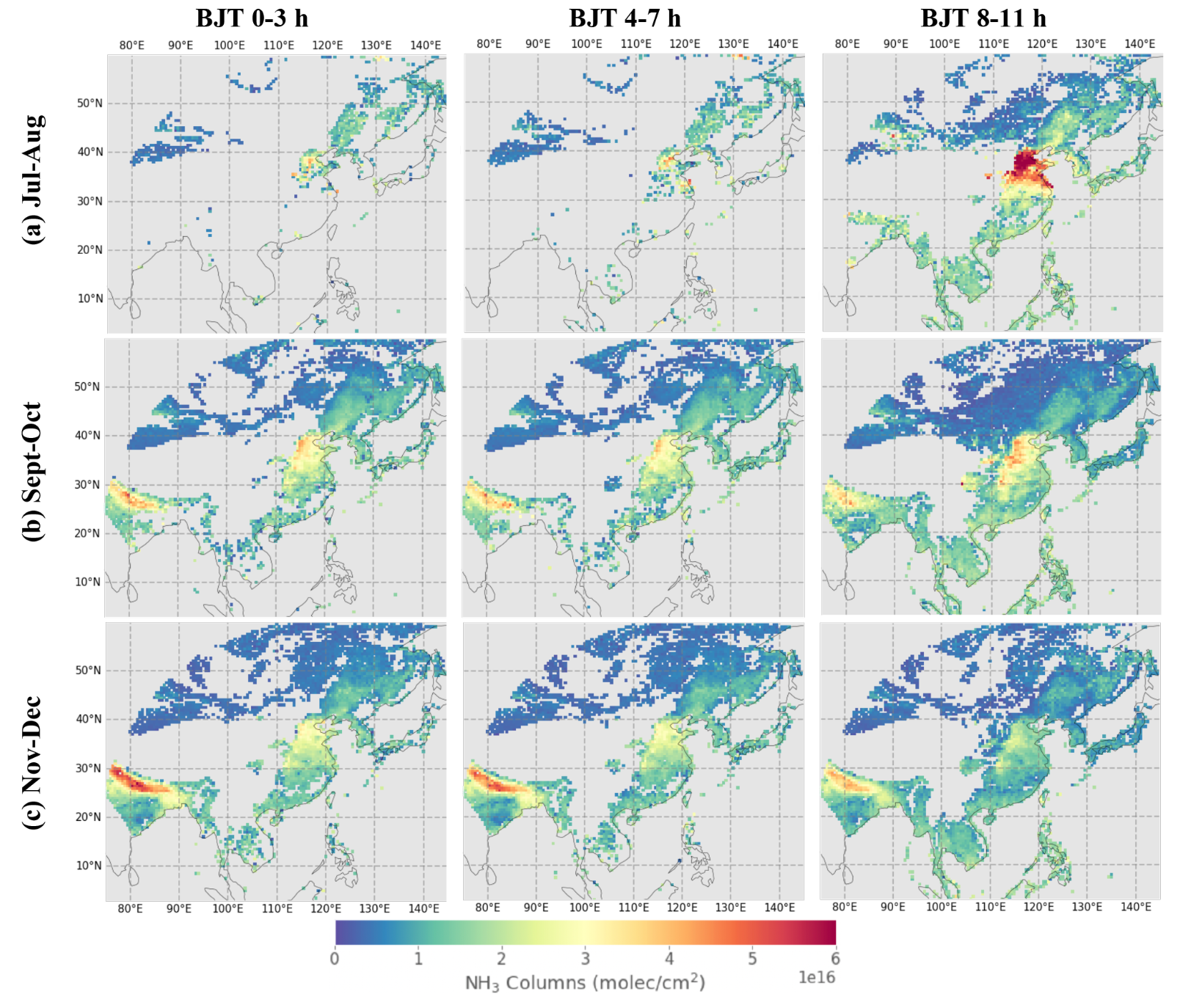
Atmospheric ammonia (NH3) is a reactive nitro- gen compound that pollutes our environment and threatens public health. Monitoring the spatial and temporal variations is important for quantifying its emissions and depositions and evaluating the strategies for managing anthropogenic sources of NH3. In this study, we present an NH3 retrieval algorithm based on the optimal estimation method for the Geostationary Interferometric Infrared Sounder (GIIRS) on board China’s FengYun-4B satellite (FY-4B/GIIRS). In par- ticular, we examine the information content based on the de- gree of freedom for signal (DOFS) in retrieving the diurnal NH3 in East Asia, with a focus on two source regions includ- ing the North China Plain and North India. Our retrieval is based on the FengYun Geostationary satellite Atmospheric Infrared Retrieval (FY-GeoAIR) algorithm and exploits the strong NH3 absorption window of 955–975 cm−1. Retrieval results using FY-4B/GIIRS spectra from July to December 2022 show that the DOFS for the majority ranges from 0 to 1.0, mainly depending on the thermal contrast (TC) de- fined as the temperature difference between the surface and the lowest atmospheric layer. Consistent with retrievals from low-Earth-orbit (LEO) infrared sounders, the detection sen- sitivity, as quantified by the averaging kernel (AK) matrix, peaks in the lowest 2 km atmospheric layers. The DOFS and TC are highly correlated, resulting in a typical “butterfly” shape. That is, the DOFS increases when TC becomes ei- ther more positive or more negative. The NH3 columns from FY-4B/GIIRS exhibit significant diurnal cycles that are con- sistent with the day–night gradient from the collocated IASI retrievals in the North China Plain and North India for the av- erages in July–August, September–October, and November– December, respectively. A collocated point-by-point inter- comparison with the IASI NH3 dataset shows generally good agreement with a small systematic difference in the summer months that may be attributed to the slight difference in a priori profiles. This study demonstrates the capability of FY- 4B/GIIRS in capturing the diurnal NH3 changes in East Asia, which will have the potential to improve regional and global air quality and climate research.
Zeng, Z.-C.*, Lee, L., Qi, C., L. Clarisse, and M. Van Damme (2023), Optimal estimation retrieval of tropospheric ammonia from the Geostationary Interferometric Infrared Sounder onboard FengYun-4B, Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 16, 3693–3713, https://doi.org/10.5194/amt-16-3693-2023.
Zeng, Z.-C.*, B. Franco, L. Clarisse, L. Lee, C. Qi, and F. Lu (2024), Observing a Volatile Organic Compound from a Geostationary Infrared Sounder: HCOOH from FengYun-4B/GIIRS, JGR-Atmosphere, 129, e2024JD041352. https://doi.org/10.1029/2024JD041352.
[4] Global carbon monoxide retrieval from the hyperspectral infrared atmospheric sounder-II onboard FengYun-3E in a dawn-dusk sun-synchronous orbit
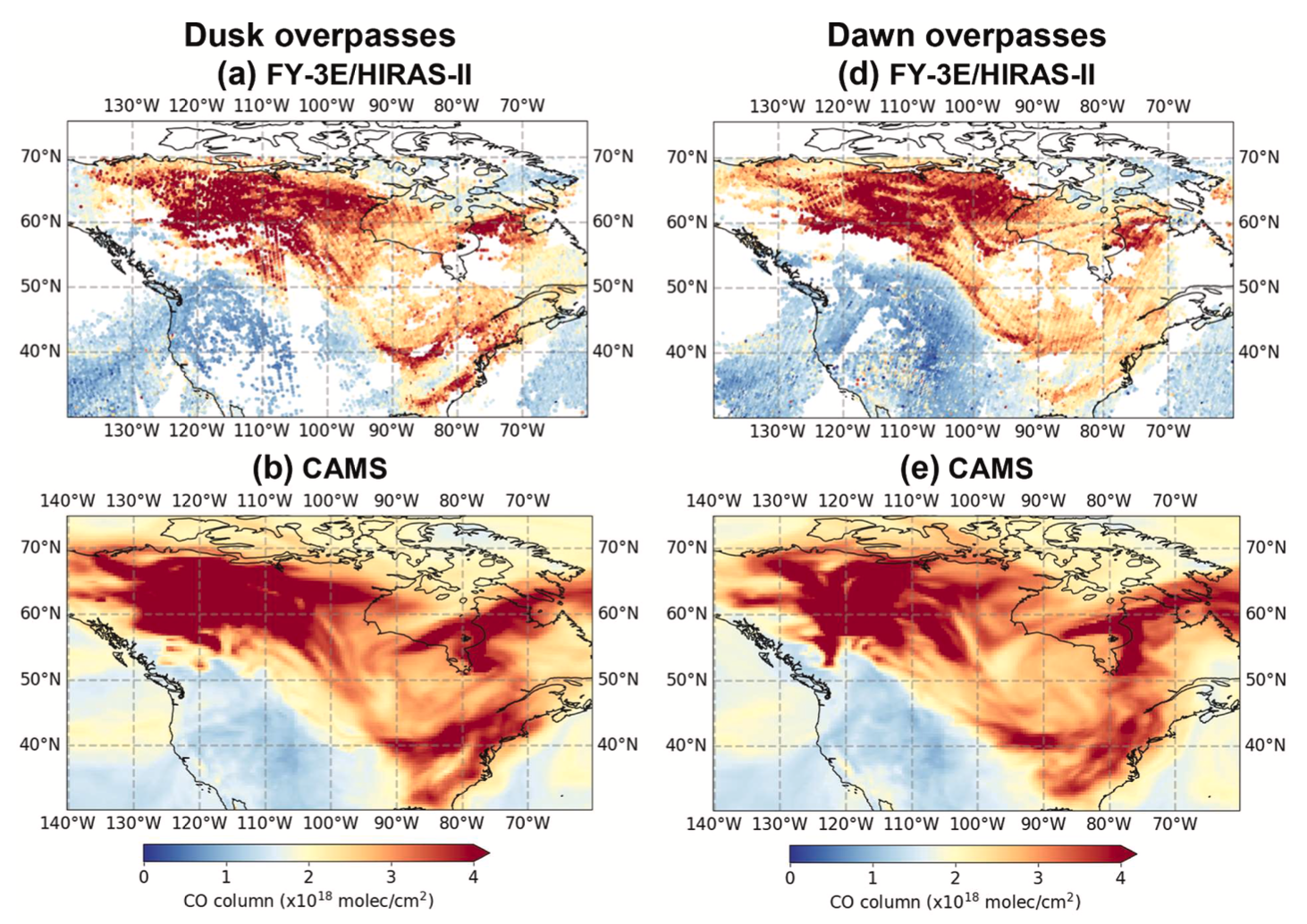
This study presents an information content analysis of the retrieval of global carbon monoxide (CO) from the 2nd generation of Hyperspectral Infrared Atmospheric Sounder on board Fengyun-3E (FY-3E/HIRAS-II), which is the world’s first dawn-dusk orbiting meteorological satellite for civilian use with equatorial overpass times at about 5:30am/pm. Using the distinctive absorption features of CO around 2145 cm-1 in the infrared band, a retrieval algorithm based on optimal estimation is first developed to retrieve the CO profiles from FY-3E/HIRAS-II. The thermal contrast, defined as the temperature difference between the surface and the lower atmosphere, is then examined for the FY-3E/HIRAS-II observations to investigate the potential sensitivity of the observations. Re- trievals of CO columns on four representative days over four seasons reveal strong enhancements from global wildfire emissions. Furthermore, the information content from the spectra, quantified by the degree of freedom for signal (DOFS), is assessed using the retrievals. The retrievals are compared with model simulations, which show good agreement. Finally, synthetic experiments are performed to investigate the impacts of thermal contrast and the vertical structure of wildfire-induced CO enhancement on the observational sensitivity. The result highlights the effectiveness of observing wildfire-induced CO enhancement during the dawn and dusk hours, even when thermal contrast conditions are not favorable. This study demonstrates the capability of FY-3E/ HIRAS-II to monitor global CO, which sheds light on the potential benefits of adding dawn-dusk orbit observations to the current global air quality observations from mid-morning and early-afternoon orbit constellations.
Z.-C. Zeng* (2025), Global carbon monoxide and formic acid observed from FY-3E/HIRAS-II in a dawn-dusk sun-synchronous orbit, Journal of Quantitative Spectroscopy and Radiative Transfer, Vol. 333, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jqsrt.2024.109336.
[5] Decadal decrease in Los Angeles methane emissions is much smaller than bottom-up estimates
Methane, a powerful greenhouse gas, has a short atmospheric lifetime ( ~ 12 years), so that emissions reductions will have a rapid impact on climate for- cing. In megacities such as Los Angeles (LA), natural gas (NG) leakage is the primary atmospheric methane source. The magnitudes and trends of fugitive NG emissions are largely unknown and need to be quantified to verify com- pliance with emission reduction targets. Here we use atmospheric remote sensing data to show that, in contrast to the observed global increase in methane emissions, LA area emissions decreased during 2011-2020 at a mean rate of (–1.57 ± 0.41) %/yr. However, the NG utility calculations indicate a much larger negative emissions trend of −5.8 %/yr. The large difference between top- down and bottom-up trends reflects the uncertainties in estimating the achieved emissions reductions. Actions taken in LA can be a blueprint for COP28 and future efforts to reduce methane emissions.
Zeng, Z.-C.*, T. Pongetti, S. Newman, T. Oda, K. Gurney, P. I. Palmer, Y. L. Yung, and S. P. Sander* (2023), Decadal decrease in Los Angeles methane emissions is much smaller than bottom-up estimates, Nature Communications, 14, 5353, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-40964-w.
[论文报道:Highlight by Caltech News and Universities Space Research Association News]
a) https://www.caltech.edu/about/news/methane-emissions-in-la-are-decreasing-more-slowly-than-previously-estimated
b) https://newsroom.usra.edu/new-study-uncovers-slower-methane-emission-reduction-in-los-angeles-challenging-previous-estimates/
Click:
The Last Update Time:..