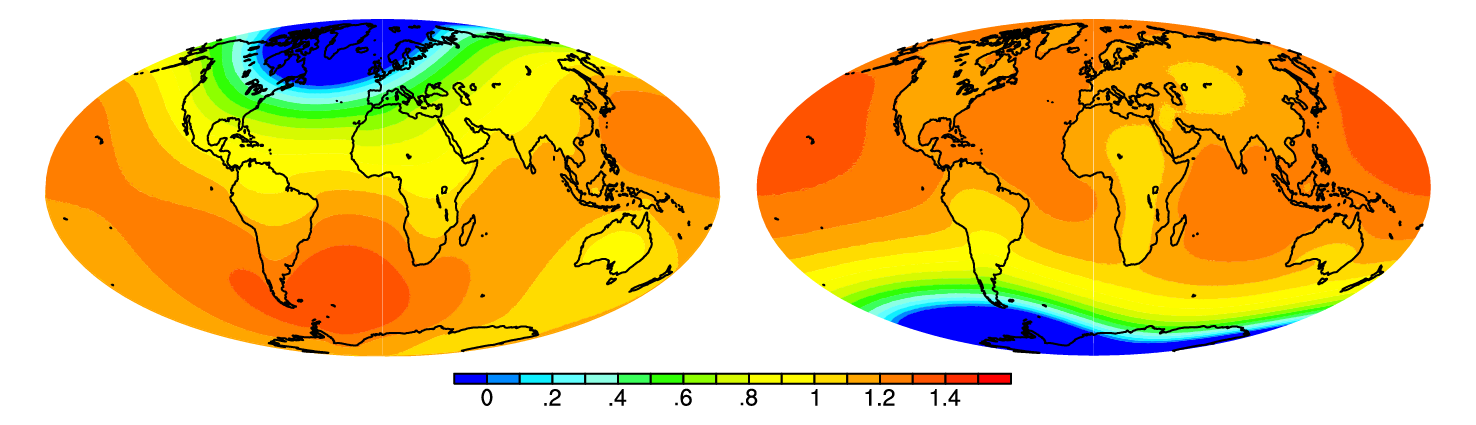
When ice sheets grow or melt, they not only just redistribute water at the Earth’s surface but also deform the solid Earth, therefore the mass distribution of the Earth is changed, which affects both the gravitational fields and the rotational state of the Earth. This has direct effect on the sea level change when Greenland ice sheet or Antarctic ice sheet melt in the future; sea level rises more for regions far from the ice sheet than for regions close to the ice sheet. Sea level can even drop for places very close to the ice sheet. The major effect on Earth rotation is to gradually shift the ice sheets from higher latitudes towards the equator.